
The second ionization energy of all of the alkaline metals is also somewhat low.
#REACTIVITY TREND OF ALKALI EARTH METALS FULL#
The alkaline earth metals have the second-lowest first ionization energies in their respective periods of the periodic table because of their somewhat low effective nuclear charges and the ability to attain a full outer shell configuration by losing just two electrons.
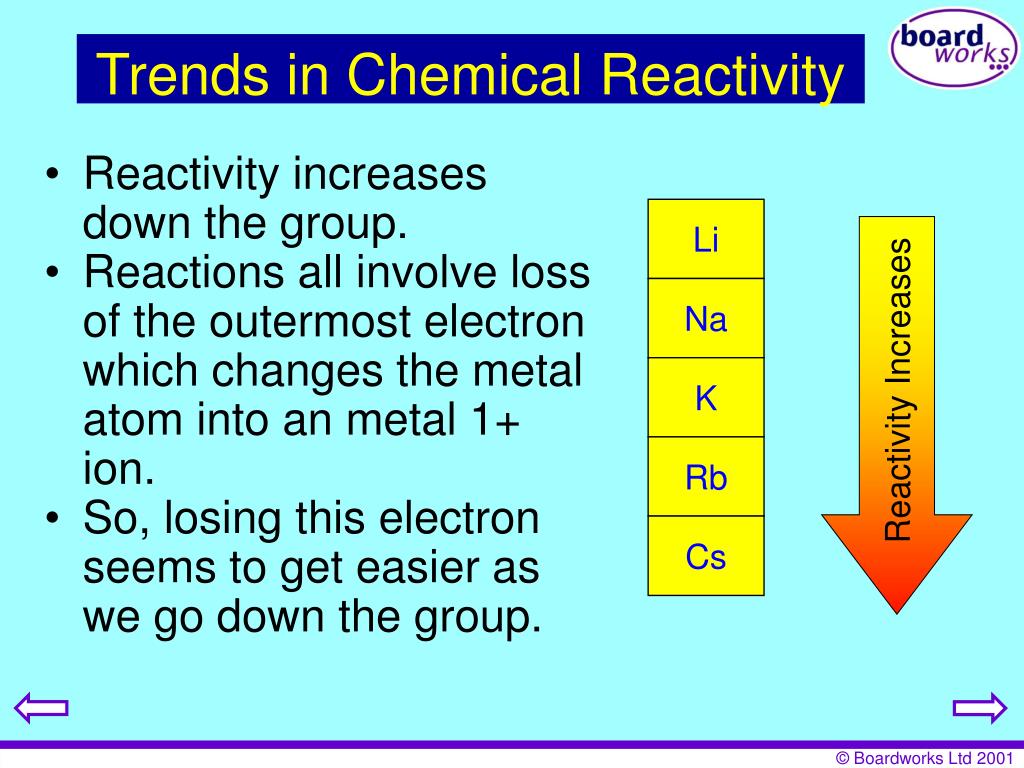
The heavier alkaline earth metals react more vigorously than the lighter ones. All the alkaline earth metals except beryllium also react with water to form strongly alkaline hydroxides and, thus, should be handled with great care. In chemical terms, all of the alkaline earth metals react with the halogens to form the alkaline earth metal halides, all of which are ionic crystalline compounds (except for beryllium chloride, beryllium bromide and beryllium iodide, which are covalent). The alkaline earth metals are all silver-colored and soft, and have relatively low densities, melting points, and boiling points. The chemistry of radium is not well-established due to its radioactivity thus, the presentation of its properties here is limited. Most of the chemistry has been observed only for the first five members of the group.

There have been experiments, all unsuccessful, to try to synthesize element 120, the next potential member of the group.Ĭharacteristics Chemical Īs with other groups, the members of this family show patterns in their electronic configuration, especially the outermost shells, resulting in trends in chemical behavior: Īll the discovered alkaline earth metals occur in nature, although radium occurs only through the decay chain of uranium and thorium and not as a primordial element. Helium itself is a noble gas and not an alkaline earth metal, though it is theorised to have some similarities to beryllium when forced into bonding and has sometimes been suggested to belong to group 2. That is, this orbital contains its full complement of two electrons, which the alkaline earth metals readily lose to form cations with charge +2, and an oxidation state of +2.

Structurally, they (together with helium) have in common an outer s-orbital which is full. The elements have very similar properties: they are all shiny, silvery-white, somewhat reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group 2 of the periodic table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
